Facilities and Location
The Chihuahuan Desert Rangeland Research Center consists of 64,000 +/- acres of rangeland. The variable stocking rate (livestock numbers) is determined by the amount of annual precipitation.
The headquarters has two homes, a small shop, livestock facilities, and a hay barn. Housing facilities at the CDRRC headquarters include a manager residence, assistant manager residence and the original ranch house. The manger residence is a 1900 sq. ft. ground set modular consisting of three bedrooms, two full bathrooms, living room, dining room, office and detached garage. The assistant manager residence is a 1480 sq. ft. site built home with two bedrooms, one bathroom, kitchen and living room. The original ranch house was built in the early 1900’s and is currently uninhabitable.
There are various outbuildings used for storage. The primary feed storage is a 48 ft. van trailer. Hand tools and consumables are stored in the 500 sq. ft. manager residence garage. There is a small shed used for saddles, tack and other equine supplies. A 20 ft. x 60 ft. pole barn used for hay storage and a 20 ft. x 20 ft. building that contains the livestock scales. Buildings used on a limited basis include an older building of rock construction and a small wood shed.
The headquarter livestock facilities are of pipe construction, except for one small portion which is wood.
Maps
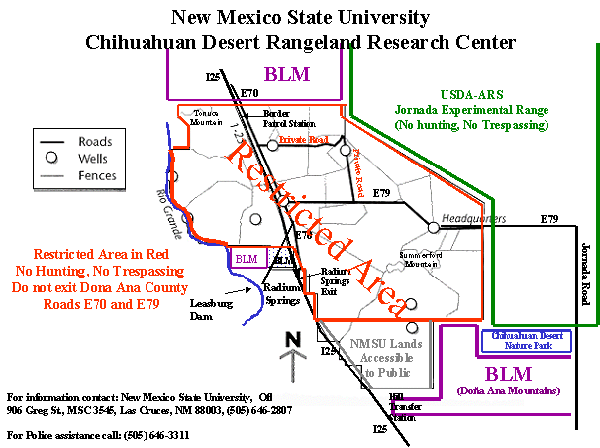
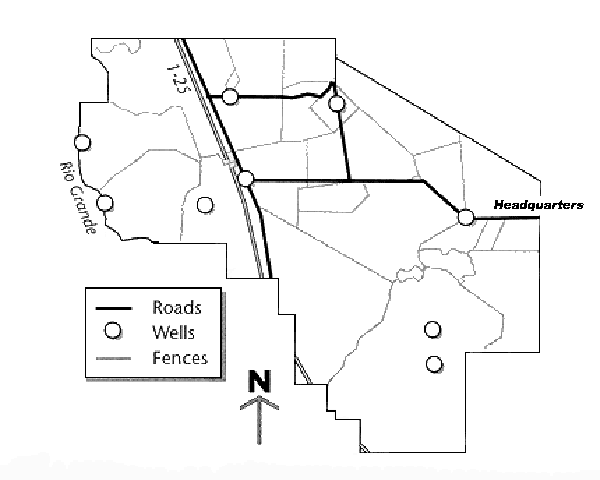
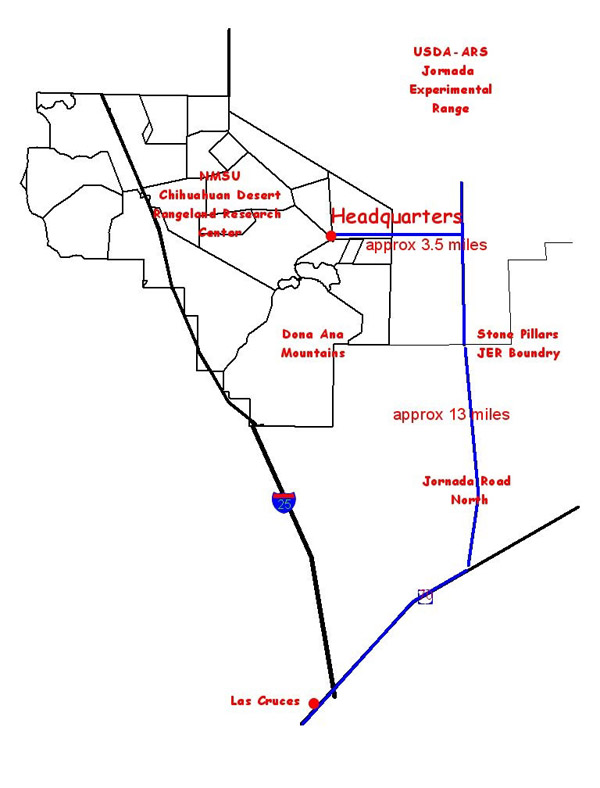
The following maps are presented to help inform users of the different areas of the CDRRC. They are intended to provide users with the boundaries and to show the diversity of range types on the CDRRC.
Click on image for larger view
Large 36" X 36" Digital Orthophoto
The Aerial View of the CDRRC is provided for researchers and interested personnel.
Pasture Boundaries
This area is used to serve the congressional mission of the CDRRC and is restricted from public access and hunting.
If you have questions regarding the above policy, please contact:
Department of Animal and Range Sciences
Location and Description
The Center is located in Dona Ana County, New Mexico, at the southern end of the Jornada Plain. Now divided by Interstate 25, the Center encompasses almost 100 square miles, with one-forth of the land west of the interstate.
 Click on image for larger view
Click on image for larger view
 Click on image for larger view
Click on image for larger view
Land on the Center varies widely, with elevations from 4,000 ft. on the Rio Grande flood plain on the west side to 5,840 ft. at the top of Summerford Mountain in the Doña Ana Mountains on the east side. the nearly levels plains of the north and central parts of the Center are on the Jornada del Muerto basin, with several small playa areas where water collects after rainfall. Soils range from sandy loams to clays overlying caliche hardpan.
Several vegetation types occur on the center. Creosote bush dominates the upper slopes of the mountains and the hills along the river. At lower elevations, the creosote bush type grades into the mesquite type that grows on sandier soils, and into the tarbush type on heavier soils. The plains area, once dominated by black grama, today has been invaded by mesquite. These mesquite stands are interspersed with snakeweed and many species of grasses and forbs.
Wildlife populations on the Center are rich and varied. Among the larger mammals are mule deer, pronghorn antelope, gemsbok, bobcat, coyote, badger, and fox. Mountain lions have been sighted. There are also many rabbit and rodent species. Several bird species migrate throughout the area, but a large number also live and nest on the rangeland. Species such as roadrunners, hawks, and occasionally golden eagles are seen on the Center. Numerous lizard and snake species also inhabit these lands.

